Table 1 Lower bounds for the number of items with the maximum score for several studies. N is the number of items that constitute the (sub)scale, S
m
is the maximum possible individual item score, n is the reported number of subjects, 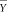 is the reported mean (sub)scale score, and L is the derived lower bound for the number of items with the maximum score. The last column lists a lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score based on L. The second highest possible item score S
m - 1 is equal to S
m- 1 for all considered (sub)scales.
is the reported mean (sub)scale score, and L is the derived lower bound for the number of items with the maximum score. The last column lists a lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score based on L. The second highest possible item score S
m - 1 is equal to S
m- 1 for all considered (sub)scales.
Scale | N | S m | n |
| L |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Checklist Individual Strength | Oxford-CFS, CDC94-UCF; Vercoulen et al. [10] | |||||
-fatigue severity subscale | 8 | 7 | 758 | 51.7 | 2805 | 46% |
-physical activity subscale | 3 | 7 | 758 | 16.9 | 0 | 0% |
-reduced motivation subscale | 4 | 7 | 758 | 17.0 | 0 | 0% |
-concentration subscale | 5 | 7 | 758 | 27.5 | 0 | 0% |
Checklist Individual Strength | CDC94-UCF; van der Werf et al. [21] | |||||
-homebound group; fatigue severity subscale | 8 | 7 | 18 | 53.6 | 101 | 70% |
-matched ambulant group; fatigue severity subscale | 8 | 7 | 32 | 52.8 | 154 | 60% |
-total ambulant group; fatigue severity subscale | 8 | 7 | 270 | 52.1 | 1107 | 51% |
-homebound group; physical activity subscale | 3 | 7 | 18 | 15.8 | 0 | 0% |
-matched ambulant group; physical activity subscale | 3 | 7 | 32 | 17.0 | 0 | 0% |
-total ambulant group; physical activity subscale | 3 | 7 | 270 | 17.6 | 0 | 0% |
-homebound group; concentration subscale | 5 | 7 | 15 | 22.4 | 0 | 0% |
Shortened Fatigue Questionnaire | van der Werf et al. [22] | |||||
-survey respondents (Dutch ME-Association members) | 4 | 7 | 1955 | 23.9 | 0 | 0% |
-research participants (CDC94-UCF) | 4 | 7 | 270 | 26.1 | 567 | 53% |
Shortened Fatigue Questionnaire | Oxford-CFS, CDC94-UCF; Alberts et al. [11] | |||||
-normative data for CFS | 4 | 7 | 445 | 26 to 27 | 890 | 50% |
Shortened Fatigue Questionnaire | CDC94-CFS; Vermeulen et al. [12] | |||||
-study group | 4 | 7 | 35 | 24.8 | 28 | 20% |
Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale | CDC88-CFS; Friedberg et al. [19] | |||||
-treatment group | 9 | 7 | 22 | 58 | 88 | 44% |
-no-treatment group | 9 | 7 | 22 | 51 | 0 | 0% |
Krupp Fatigue Severity Scale | CDC88-CFS; DeLuca et al. [23] | |||||
-subjects with concurrent axis 1 psychiatric disorder | 9 | 7 | 12 | 58.5 | 54 | 50% |
-subjects without concurrent psychiatric disorder | 9 | 7 | 21 | 57.2 | 67 | 36% |
14-item Chalder Fatigue Scale | Oxford-CFS; Wearden et al. [15] | |||||
-'exercise and fluoxetine group' | 14 | 3 | 33 | 35.9 | 261 | 56% |
-'exercise and placebo group' | 14 | 3 | 34 | 33.7 | 194 | 41% |
-'exercise control and fluoxetine group' | 14 | 3 | 35 | 34.4 | 224 | 46% |
-'exercise control and placebo group' | 14 | 3 | 34 | 34.0 | 204 | 43% |
14-item Chalder Fatigue Scale | Oxford-CFS; Fulcher et al. [16] | |||||
-exercise group | 14 | 3 | 33 | 28.9 | 30 | 6% |
-fiexibility group | 14 | 3 | 33 | 30.5 | 83 | 18% |
11-item Chalder Fatigue Scale | CDC94-CFS; Jason et al. [13] | |||||
-physical subscale | 7 | 3 | 15 | 18.40 | 66 | 63% |
-mental subscale | 4 | 3 | 15 | 9.13 | 17 | 28% |
11-item Chalder Fatigue Scale | CDC94-CFS; Wallman et al. [17] | |||||
-exercise group; physical subscale | 7 | 3 | 32 | 11.6 | 0 | 0% |
-exercise group; mental subscale | 4 | 3 | 32 | 6.3 | 0 | 0% |
-relaxation/flexibility group; physical subscale | 7 | 3 | 29 | 11.4 | 0 | 0% |
-relaxation/flexibility group; mental subscale | 4 | 3 | 29 | 5.6 | 0 | 0% |
11-item bimodal Chalder Fatigue Scale | Oxford-CFS and CDC94-CFS; Deale et al. [20] | |||||
-cognitive behavior therapy group | 11 | 1 | 30 | 10.1 | 303 | 92% |
-relaxation group | 11 | 1 | 30 | 9.3 | 279 | 85% |
11-item bimodal Chalder Fatigue Scale | Oxford-CFS; Powell et al. [18] | |||||
-control group | 11 | 1 | 34 | 10.6 | 360 | 96% |
-minimum intervention group | 11 | 1 | 37 | 10.4 | 385 | 95% |
-telephone intervention group | 11 | 1 | 39 | 9.9 | 386 | 90% |
-maximum intervention group | 11 | 1 | 38 | 10.2 | 388 | 93% |
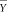 is the reported mean (sub)scale score, and L is the derived lower bound for the number of items with the maximum score. The last column lists a lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score based on L. The second highest possible item score S
m - 1 is equal to S
m- 1 for all considered (sub)scales.
is the reported mean (sub)scale score, and L is the derived lower bound for the number of items with the maximum score. The last column lists a lower bound for the percentage of items with the maximum score based on L. The second highest possible item score S
m - 1 is equal to S
m- 1 for all considered (sub)scales.